VBA programs execute code-lines in a sequential manner. However, situations often arise where you need to skip ahead or circle back to a code-line. That is where jump statements like the Exit statement come into play. They are of immense importance as they allow the non-sequential transfer of control (i.e., program execution).
Introducing the Exit Statement
The Exit statement instantly leaves a code-block. Also, it transfers control to the code-line right after the block’s closing statement.
However, it only works for specific blocks. These include Do and For loops, and Function, Subroutine (i.e., Sub), and Property procedures. The table below shows its syntax for each of these blocks.
| Syntax | Immediately Exits From | Transfers Control To |
|---|---|---|
| Exit Do | Do While – Loop statement; Do Until – Loop statement; Do – Loop While statement; Do – Loop Until statement. | Code-line directly following the block’s closing statement, i.e. Loop, Loop While, or Loop Until. |
| Exit For | For – Next statement; For Each – Next statement. | Code-line directly following the block’s closing statement, i.e. Next. |
| Exit Function | Function statement | Code-line directly following the statement that invoked (i.e., called) the Function. |
| Exit Sub | Sub statement | Code-line directly following the statement that invoked (i.e., called) the Subroutine. |
| Exit Property | Property statement | Code-line directly following the statement that invoked (i.e., called) the Property. |
Use in other Jump Statements
By themselves, Exit statements rarely prove useful. They are typically encased in Selection statements that set conditions for their execution. It is common to find them in other types of jump statements.
Exit statement within the GoSub Statement
We have detailed the GoSub statement in a separate article. The image below (taken from that article) shows its logic flowchart. The Exit statement’s utility as part of the GoSub statement is clear.
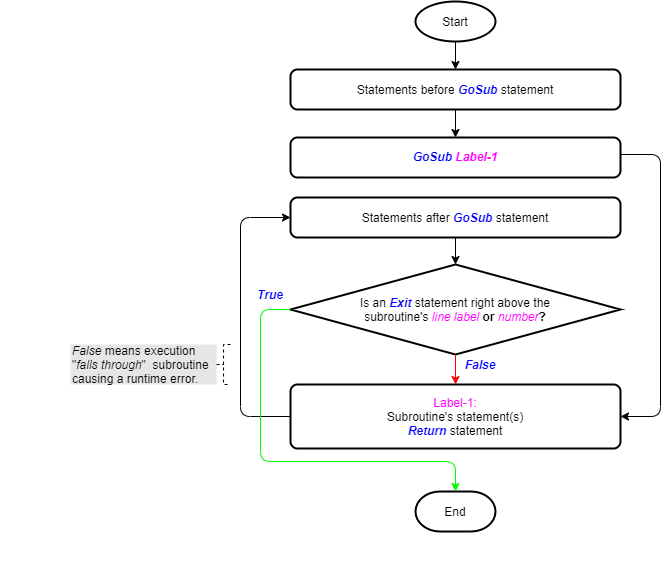
Exit statement within the On – GoSub Statement
We have explored the On GoSub statement in another article. The image below (taken from that article) shows its logic flowchart. The Exit statement’s usefulness as part of the On GoSub statement stands out.
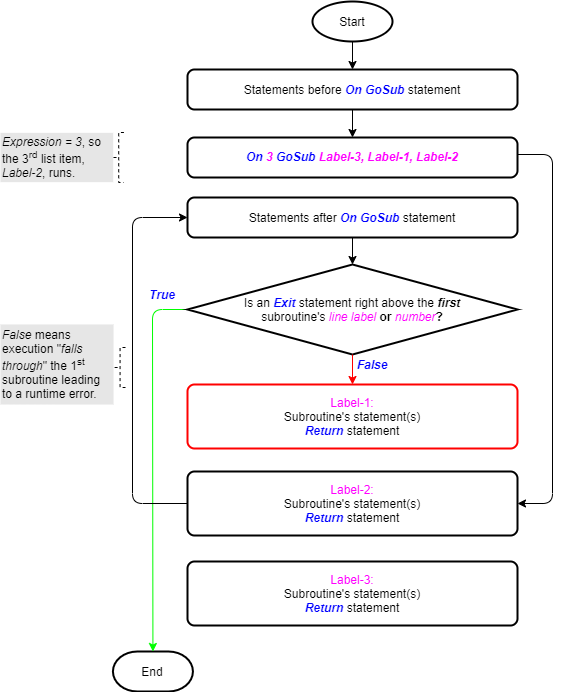
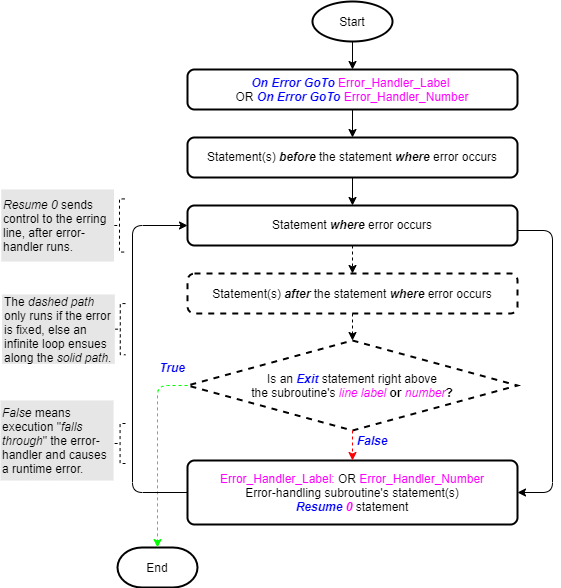
Exit statement within the On Error GoTo Statements
The On Error GoTo Line/Label statements are explored in a standalone article. The images below (taken from that article) show their logic flowcharts. You can see the importance of the Exit statement as part of the On Error GoTo Line/Label statements.
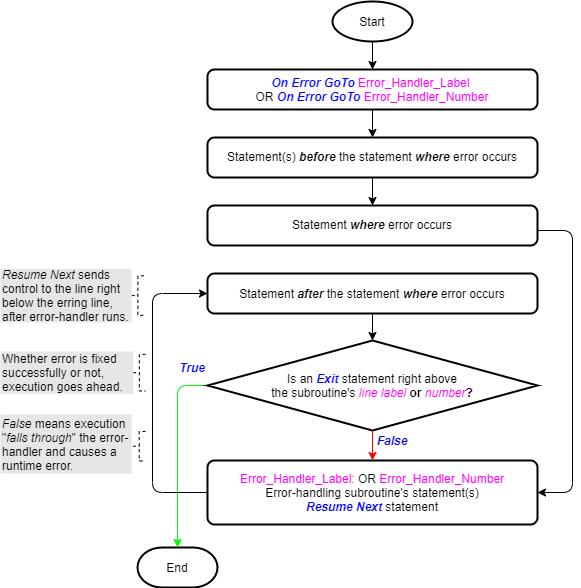
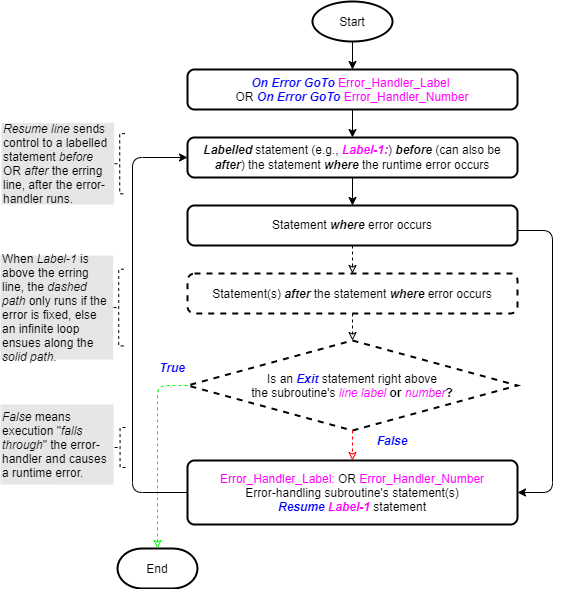
Use in Iteration Statements
The Exit statement also finds common use as part of VBA iteration statements. There are two types of VBA iteration statements, For and Do loops.
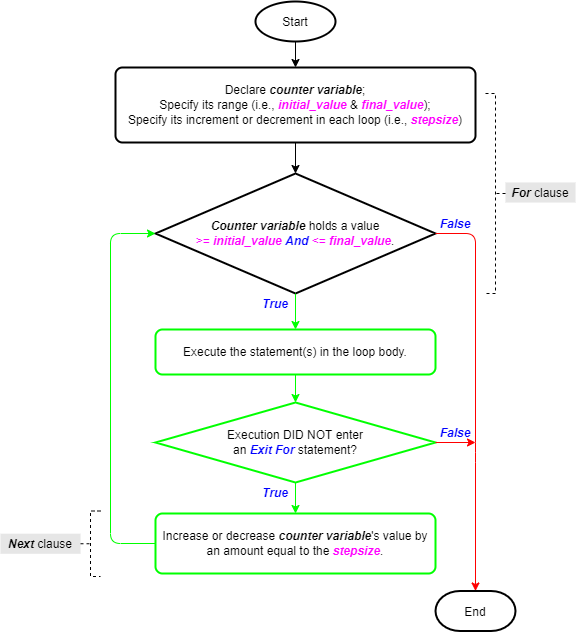
Exit statement within For Loops
The For – Next statement is detailed in a separate article. The image below (taken from that article) shows its logic flowchart. The Exit statement’s utility as part of the For – Next statement is clear.
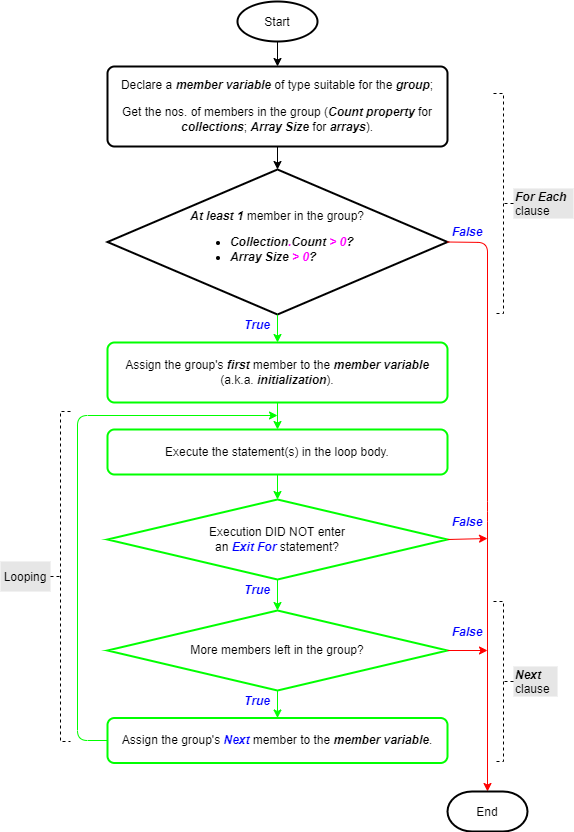
The For – Each statement is discussed in-depth in a standalone article. The image below (taken from that article) shows its logic flowchart. The Exit statement’s usefulness as part of the For – Each statement stands out.
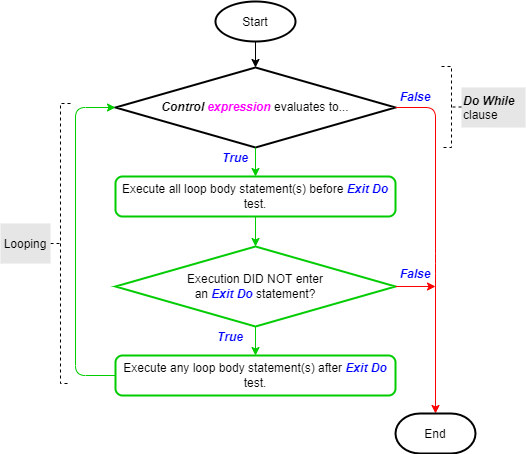
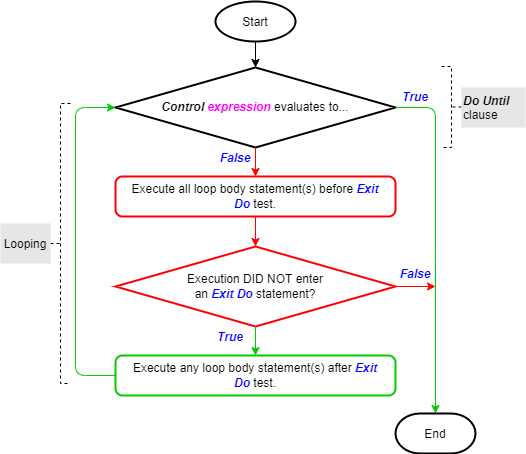
Exit statement within the Do Loops
We have explored the Do While and Do Until statements in another article. The images below (taken from that article) show their logic flowcharts. You can see the importance of the Exit statement as part of these iteration statements.


![The While – Wend statement’s syntax. Square brackets, [ ], indicate optional items.](https://masterofficevba.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/While_Wend_Statement_Syntaxnew.png)
![The Do – Loop Until statement’s syntax. Square brackets, [ ], indicate optional items while vertical bars, |, indicate mutually exclusive items.](https://masterofficevba.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/Do_Loop_Until_Statement_Syntaxnew.png)
![The Do – Loop While statement’s syntax. Square brackets, [ ], indicate optional items while vertical bars, |, indicate mutually exclusive items.](https://masterofficevba.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/Do_Loop_While_Statement_Syntaxnew.png)
![The Do Until – Loop statement’s syntax. Square brackets, [ ], indicate optional items.](https://masterofficevba.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/Do_Until_Loop_Statement_Syntaxnew.png)





![The While – Wend statement’s syntax. Square brackets, [ ], indicate optional items.](https://masterofficevba.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/While_Wend_Statement_Syntaxnew-300x163.png)
![The Do – Loop Until statement’s syntax. Square brackets, [ ], indicate optional items while vertical bars, |, indicate mutually exclusive items.](https://masterofficevba.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/Do_Loop_Until_Statement_Syntaxnew-300x163.png)